Introduction (circa 2024)
I used to train transformer models before it became mainstream. Comparing to ChatGPT and models alike, this one is very unimpressive, one can even say pathetic. But let’s not forget that the work was done in 2020 by a mere 4th year student using free datasets and a 10 bucks google colab subscription. The code was mostly composed of snippets taken from random people on gihub, fixed and modified on the run. With all these circumstances I’m even somewhat surprised that it worked at all.
Problem statement
In today’s world, there is an incredible amount of textual information on any topic, and it becomes increasingly difficult for a person to choose only the one that is needed right now. In order to reduce the time of searching and understanding information, the task of text summarization, which is also called autoreferencing, appeared in the science of natural language processing. The purpose of summarization algorithms is to extract the main thoughts and ideas from the text flow and create a new human-readable text based on them.
The following tasks were solved in the work: 1) Evaluation of summarization results for neural networks with different configurations 2) Evaluation of the results of neural networks with different input data, quality dependence on data structure 3) Checking the possibility of applying pre-trained neural networks to these data
Method overview
LSTM
One of the first effective models of abstract summarization was the recursive Encoder-Decoder model, which consists of LSTM layers. The Long-Short Time Memory layer allows you to store the important context of sentences, depending on the words and their meaning, not just the distance between them. The model is divided into two parts: encoder and decoder. The encoder transforms the input text into an embedding vector of a fixed size, and the decoder processes this vector and creates the corresponding abbreviated text.
The scheme of such a model is shown below:

The efficiency of the LSTM layer is due to the fact that with each new word the internal state changes according to the context. For example, a new noun can change the gender context and the following verb is transformed according to this gender, but other information from the internal state will not change. This becomes real thanks to the so-called gates, which filter which information is removed from the context at each step, and which is added. The matrices that are required for the operation of these gates are formed in the process of machine learning.

It turned out that this model shows good results only for short texts. It is difficult to fit all possible meanings of large texts in a vector of fixed size, even if this fixed size exceeds a thousand. Also, LSTM layers lose the necessary context information over time.
Attention
Later, various modifications to Encoder-Decoder models with LSTM layers were invented. One of the best results was demonstrated using the Attention approach. This approach is based on the idea that some words from the input text and words from the output text are logically related to each other, to a greater or lesser degree. The scheme of the model with such a layer is shown below:

In the diagram, in the lower row, the steps of the encoder are marked in blue, and the steps of the decoder are marked in red. It is in the attention layer that the interaction of the decoder states and the words of the initial text takes place. The visualization of such connections is shown below:

The model learns to detect these dependencies during the machine learning process. The Attention layer in such models is inserted after the lstm layers or between them and learns to highlight from the processed data those important parts that will be transformed into the correct abbreviated text. This approach significantly improved the results of Encoder-Decoder models.
Self-attention
In 2017, an article was published in which a model was proposed that would be based only on attention principles and exclude recurrent or convolutional layers. This class of models was named Transformer and combines several encoders and decoders connected together.
The scheme of such a model is shown below:

In each of the encoders and decoders there is a Self-Attention layer that learns to detect dependencies between words in the text. The Self-Attention principle generalizes Attention and applies to the text in relation to itself. With the help of special matrices, query, key and value vectors are calculated for each word. Using these vectors, the value of attention between different words in the text is obtained, which is an indicator of logical connections. This allows you to get a better understanding of the context and highlight the most important parts of the text.
The article considered the task of text translation and this model demonstrated better results than previously considered and required less time and resources for training.
Technical implementation
Text preparation
In almost every natural language, the same thought can be written in several different ways. This greatly complicates the work of any program, because a neural network, unlike people, does not know, for example, which words are synonyms or which pronouns refer to what. Most of these dependencies can be learned by the neural network in the learning process, but the more such complexities, the more time and resources will be required. Thus, the question arises: is it possible to reduce the number of these ambiguities. Since the texts in English were used in this work, the preprocessing can consist of the following steps:
- Removal of special characters
- Lower case
- Expansion of abbreviations
- Deleting stop words
- Lematization of words
But some of them can be harmful. Stop words do not carry meaning, but they connect the meaning and form a context. They are needed for the summarization task, because they can even be part of the correct result. Lematized words make processing much easier, but grammatical correctness of sentences is lost. Since the result of the program should be a grammatically and lexically correct text, this step is unnecessary for the task of summarizing the text. Thus, text preprocessing will consist of three steps: removal of special characters, reduction to lower case and expansion of abbreviations.
Using embedding vectors (Word2Vec)
One of the main problems of one-hot encoding with word-classes is the high dimensionality and lack of connections between words. These problems are solved by other algorithms for building embedding vectors. Such vectors have a fixed size and can be linearly dependent, but these dependencies have been found to reflect real semantic relationships between words in natural language. The construction of such vectors is a non-trivial task and there are several different methods of obtaining them. The main two are methods based on CBOW (Common Bag Of Words) and Skip-Gram. CBOW aims to predict a word by its context, while Skip-Gram aims to predict the context by word. Thus, when training a neural network to perform these tasks, it is possible to obtain vectors for each word that would correspond to their context. The scheme of the CBOW training model is shown below, where the size of the context for training is taken equal to three. The Skip-Gram scheme of the model is built on similar principles, but works in the opposite direction.

The structure of the Transformer model
The Transformer model consists of an encoder and a decoder. The encoder accepts a vector of text as input and converts it into a vector of continuous representation. The decoder accepts this vector as input and generates the output of the model - the probability of the next word. The generation of a complete answer consists of several steps and the results of the previous step are accepted by the decoder as an additional input. A more detailed structure of the model construction is shown below:

The encoder consists of several identical blocks, each of which contains 2 layers: an attention layer and a fully connected direct propagation layer. After each of these layers, normalization occurs with addition according to the formula
\[y=Norm(x + Layer(x))\]The decoder block has a similar structure, but with an additional attention layer, which accepts as input the result of the encoder block. Also, the attention layer that receives the decoder input is modified by masking the following words. This modification ensures that each word depends only on previous words.
Self-Attention layer
Self-attention layers are a key element of the Transformer model, so it’s important to understand exactly how they work. The first step in this layer is the creation of three vectors: query, key, value for each input word. These vectors are built by multiplying the word vector by the matrix according to formulas below. In the process of machine learning, the optimal values of these matrices are formed. The vectors q, k and v are usually smaller in size than the input vector, because they can store enough information and do not increase the running time.
\(q_{i}=x_{i}*Wq\) \(k_{i}=x_{i}*Wk\) \(v_{i}=x_{i}*Wv\)
These vectors do not have a clear meaning, but from the calculation formulas in the following steps, you can understand what role they play. For each vector qi, the vector of products with all other vectors kj is calculated. After that, the vector is divided by the square root of the dimension of the vectors and the softmax function is applied to it, together this will form the formula
\[s_{i} = softmax([q_{i}*k_{1}, ... , q_{i}*k_{n}]/8)\]Thus, for each word we get the value of abstract interaction with all others, which can be called attention. Each of these values is multiplied by the corresponding value vector and the resulting vectors are added according to the formula
\[z_{j}=\sum_{i=1}^{n} x_{i}*v_{j}\]Such calculations are performed for each input vector, so we obtain a vector zi for each input xi. All these formulas can be written in the matrix form given in formula below for convenience and speed of calculation. Visual representation of the calculation scheme is also provided.
\[Z = softmax((Q*K^{T}) /\sqrt{Dim})*V\]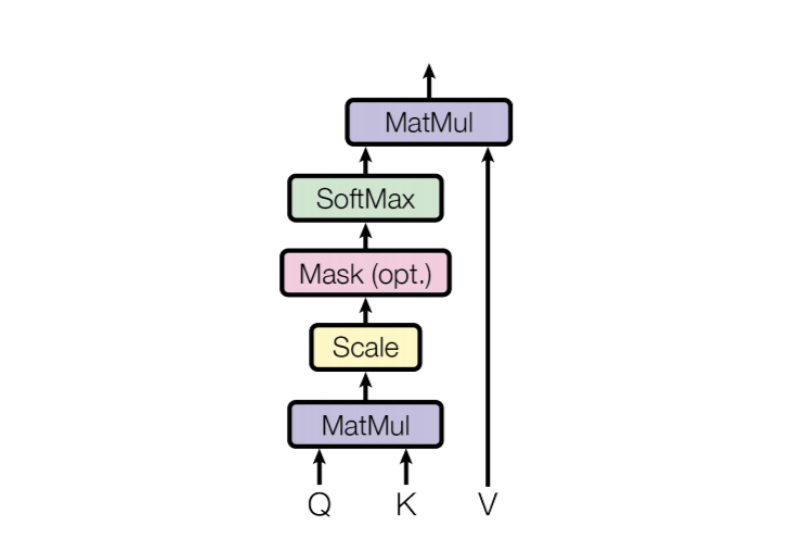
Interpretation
Behind these calculations hides an intuitive idea of how the human brain forms knowledge about the context of a sentence. For example, it is possible to determine which word replaces a pronoun only by looking at other words that are meaningfully related to them. For each adjective, there is one or more nouns to which they refer, but when written, this is not indicated in any way except for word order. The human brain can correctly determine these dependencies on the basis of many previously read sentences. The idea of the self-attention method is to reproduce these relationships in a neural network. The interpreted results of calculations in the trained self-attention layer are presented on the example of the sentence “The animal didn’t cross the street because it was too tired” from the English language.

It can be seen from the example that for the pronoun “it” the meaning of the connection with the phrase “the animal” is greater than the others, which corresponds to the perception of this sentence by a person. These relationships are expressed in formula form by the vector si. For further layers, it is more difficult to interpret the results, but the logic remains the same. The model learns to count how much attention each element has to others and thus forms a context.
Multi-headed Self-Attention layer
During research, it was found that doing calculations with large vectors is less efficient than doing several calculations with different sets of matrices Wq, Wk, Wv. Therefore, a multi-headed Self-Attention layer was proposed, which would combine more than one calculation module. The scheme of such a layer is shown below.

In addition to reducing the asymptotic complexity of the algorithm, calculations in these sublayers can be performed in parallel, which allows more optimal use of computer resources. The results of all independent calculations are concatenated into one large matrix and multiplied by the Wo matrix according to formula
\[mZ = concat(Z_{1}, … , Z_{h})Wo\]where Zi is the calculation result of the self-attention method in the ith sublayer, h is the number of sublayers, Wo is a matrix that returns the concatenated matrix to the desired size. It is formed and reaches optimal values in the process of machine learning.
The interpretation of the work of the multi-headed self-attention layer is similar to the interpretation of the simple self-attention layer, except that different sub-layers show different dependencies on different parameters, which are not always easy to understand from a human point of view.
Training and evaluation
Dataset #1: CNN/Dailymail
One of the classic examples of datasets for text summarization and other natural language processing tasks is news. They are well structured and have no grammatical errors, the title is the result of summarization. The CNN/DailyMail dataset consists of news on various topics and has the following properties:
| Number of texts | 4396 |
| Approximate number of texts with limited vocabulary | 4396 |
| Average text size | 350 |
| Average header size | 50 |

Dataset #2: Amazon Fine Foods Reviews
The Amazon Fine Foods Reviews collection consists of reviews from real people in the form of a short review and an extended comment. A summarized comment on the product will be a short review corresponding to it. The difference between this dataset and the news dataset is that all users have different styles of expressing opinions in abbreviated form. The properties of this dataset are as follows:
| Number of texts | 39356 |
| Approximate number of texts with limited vocabulary | 10000 |
| Average text size | 340 |
| Average header size | 20 |

Dataset #3: Cryptocurrency News
The dataset is similar in structure to CNN/DailyMail, but with news on only one topic. Therefore, the texts have less lexical diversity and a smaller dictionary size. This allows using a larger number of tests with limited resources. Properties of this data set:
| Number of texts | 28069 |
| Approximate number of texts with limited vocabulary | 20000 |
| Average text size | 700 |
| Average header size | 55 |

Evaluation
The results of the model on the Amazon Fine Foods Reviews dataset according to ROUGE metrics are shown in the table below:
| Rouge-1 | 0.19 |
| Rouge-2 | 0.03 |
| Rouge-L | 0.19 |
The rates are quite low, but subjectively a large number of answers seem correct. Such a big difference between objective and subjective indicators is the difference in thinking of different people. For each comment, you can come up with several short reviews, all of which could have been written by real people. But for such a system of metrics, the synonyms “good” and “great” are completely different things, so comparing two synonymous reviews can give a result equal to 0 by all metrics. Several examples of the program’s operation:

For other two datasets results are similar: metrics are low, but generated headlines make sense.
Performance studies
In the previous section, the results obtained experimentally were demonstrated, so there is an opportunity to improve them with the correct choice of parameters and configuration of the model. The Cryptocurrency News dataset was chosen for the study because it showed the best objective scores and is suitable for the task in terms of subjective indicators.
The number of epochs of machine learning significantly affects the effectiveness of the model. If the number of epochs is insufficient, the model will not be able to fully form the required dependencies. With a large number of epochs, the model can learn incorrect dependencies that are specific only to specific samples from the training sample, but not specific to samples from the testing sample. This situation is called retraining and negatively affects the model’s effectiveness on new data. The dependence graph of ROUGE metrics on the number of epochs is shown below:

The graphs are built for a single configuration of the model and for a single sample of data, but from the graph it can be assumed that on average the optimal number of epochs should be in the range of 25-30 epochs.
The amount and quality of the training data has a very large impact on the performance of the model after training. Increasing the size of the dataset while maintaining quality should improve or slightly change the metrics’ performance. This is confirmed by the research results:

Conclusion
In the course of the research, the results of the model’s operation on various datasets were analyzed, objective and subjective indicators were compared. The specificity of the task and the features of the model based on the self-attention principle complicate the process of evaluating efficiency. Sometimes the model can produce answers that are correct from the human point of view, which do not match the original ones, and vice versa. During the research, it was found that the size of the training data is of great importance for the quality of the result. Potentially, increasing the volume of these data can improve the results obtained in the work. For the possibility of increasing the volume, it is necessary to use computers with greater computing power and more efficient vectorization algorithms.
